10 bladder facts
In this article we will describe 10 facts about the bladder. Let’s start with the basics.
1. Basics – the bladder is a hollow, triangular-shaped muscular organ located in the lower abdomen (the pelvis). Its function is to act as a reservoir for urine (expanding as it fills up), before it is removed from the body through urination (weeing).
It is bladder is connected to the kidneys through two tubes called ureters, which transport urine from the kidneys to the bladder. It is an intrinsic part of the urinary tract.
Although you do not control how your kidneys function, you can control when to empty your bladder.
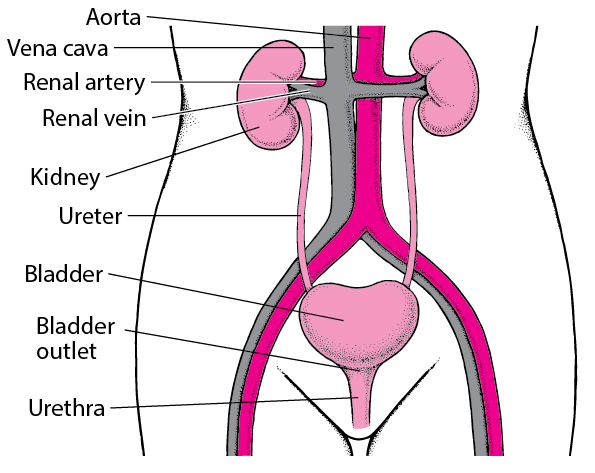 Urinary tract
Urinary tract
2. Position – in males, the bladder is located in front of the rectum and just below the prostate gland. In females, it is located in front of the uterus and above the vagina.
 Position of female bladder
Position of female bladder
3. Primary function – stores urine produced by the kidneys before it is eliminated from the body through the urethra.
Note. Urine is a. sterile (not infected; there are normally no bacteria in it), b. not dirty, and c. not dangerous if you touch it (due to a + b).
4. Volume – average adult bladder volume is 300 (200-400) mls – i.e. mm .. quite small, yes = a can of coke.
5. Frequency of urination – the average adult urinates approximately 6-7 times a day, depending on fluid intake.
This will lead to a urine output of say 6.5 x 300 mls = about 2L (well 1950 mls!), based on drinking 2.5L a day (500 mls insensible loss).
How much should you drink? There is no normal (or desired) fluid intake. But about 2.5L is fine. If you drink more than that, you will urinate more times a day.
6. Lining – the bladder is lined specialised type of cells called transitional epithelial cells, which allow the bladder to stretch as it fills with urine.
7. Sensation needing to urinate – is triggered when the bladder is about half full. This is due to the activation of nerves in the bladder wall that send signals to the brain.
8. Muscle – of the bladder wall is a smooth muscle called the detrusor muscle. It contracts to expel urine during urination.
9. Duration of urination – interestingly, mammals empty their bladders on average for 21 seconds (standard deviation 13 seconds), despite a difference in bladder volume from 0.15 ml (mouse bladder) and 300 ml (human) to 18 L (elephant) and 300 L (blue whale).

10. Problems – that can affect the bladder include urinary incontinence (involuntary leakage of urine), urinary tract infections (UTIs), bladder stones, and bladder cancer (red flag symptom = macroscopic haematuria).
Note. Most uncomplicated UTIs are bladder infections, hence called cystitis.
Summary
We have described 10 bladder facts. We hope it has been helpful.

