10 heartburn facts
In this article we will describe 10 facts about heartburn.
Key Points
- Heartburn is a very common condition, affecting up to 25% of UK adults.
- Heartburn is a burning pain in the chest or upper abdomen.
- The cause of heartburn is unknown. But it it is thought to occur when stomach acid flows up into the oesophagus.
- Lifestyle changes and over-the-counter medications may be effective in managing longterm heartburn. Though the pain usually stops in acute attack with no treatment.
- Severe or persistent heartburn may require further investigation and treatment.
- What is strange is that for such a common condition little is known about it’s aetiology, and there are few proven treatments.
1. Definition
- Heartburn is a burning pain in the chest or upper abdomen.
- It may be caused by stomach acid travelling up into the oesophagus.
- It is also known as ‘acid reflux’, or gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD).
What’s in a name?
Note 1. ‘Heartburn’ is a confusing name as it is not a heart disease. And it’s not a burn.
Note 2. Other names such as ‘indigestion’ and ‘dyspepsia’ are vague and should be avoided.
Note 3. It’s a bit like cramp actually. Most of us get it. But what is it!?
2. Epidemiology
- Heartburn affects up to 25% of UK adults.
- It is more common in women and people over 40.
- It is also more common in people who are overweight or obese.
3. Risk Factors
- Being overweight or obese
- Lying down after eating
- Wearing tight clothing
- Spicy foods, fatty foods, chocolate, caffeine, alcohol, and carbonated drinks or large meals can trigger heartburn.
- Stress can sometimes exacerbate heartburn.
4. Causes
The precise cause of heartburn is unknown. Here are current theories.
- Weak lower oesophageal sphincter (LES): The LES is a ring of muscle that acts as a valve between the oesophagus and stomach. If it doesn’t close properly, stomach acid can escape into the oesophagus, causing oesophagitis. This is known as ‘reflux oesophagitis’.
- Hiatus Hernia: This condition occurs when the upper part of the stomach bulges through the diaphragm into the chest cavity, which can lead to acid reflux.
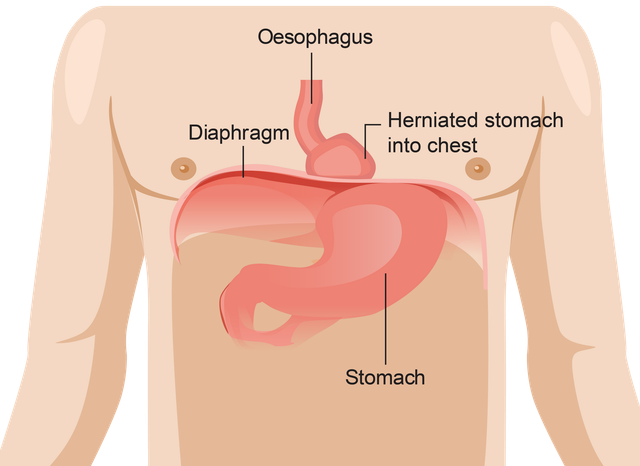
Hiatus hernia
- Medication: Like certain anti-inflammatory drugs (e.g. ibuprofen, aspirin), blood pressure medication, and muscle relaxants, can contribute to heartburn.
- Pregnancy: Hormonal changes and pressure on the stomach from the growing foetus can cause heartburn in pregnant women.
5. Symptoms
The main symptom of heartburn is a burning sensation in the chest and upper abdomen. The pain may worsen when lying down or bending over, after eating or at night.
Other symptoms may include:
- A bitter or sour taste in the mouth.
- Difficulty swallowing.
- A cough.
- A hoarse voice.
6. Diagnosis
- Heartburn is a clinical diagnosis – i.e. based on symptoms. However, if symptoms are severe or persistent, further investigation may be needed, such as an upper gastrointestinal endoscopy.
Investigation
Further investigation may include:
- Upper gastrointestinal endoscopy: This involves inserting a thin, flexible tube with a light and camera into the oesophagus to look for any damage.
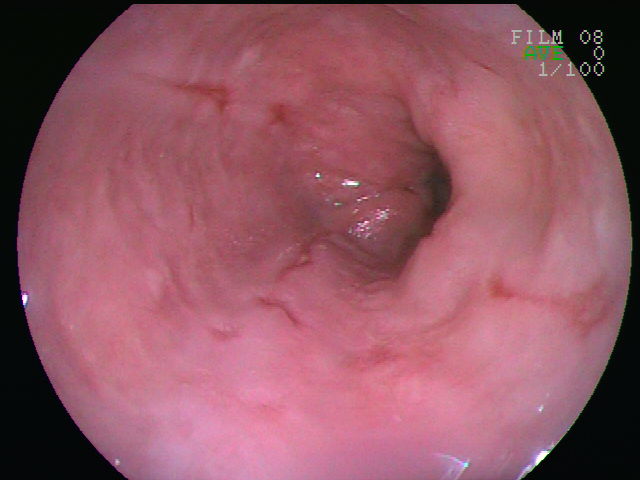
Oesophagitis on an endoscopy
- Oesophageal pH monitoring: This involves inserting a small probe into the oesophagus to measure the amount of acid present.
- Barium swallow: This involves drinking a barium solution and then having X-rays taken to look for any abnormalities in the oesophagus.
Differential Diagnosis
Other conditions that can cause similar symptoms to heartburn include:
- Angina – may be precipitated by exercise, relieved by rest, and radiates to the left arm, neck or back. This helps to distinguish it from heartburn.
- Peptic ulcer disease.
- Gall bladder disease.
- Oesophageal cancer.
7. Treatment
The treatment for heartburn depends on the severity of the symptoms. In many cases, lifestyle changes and over-the-counter medications are all that is needed.
Lifestyle changes that may help include:
- Losing weight if you are overweight or obese.
- Eating smaller, more frequent meals.
- Avoiding fatty, spicy, and acidic foods.
- Avoiding alcohol and caffeine.
- Quitting smoking.
- Wearing loose-fitting clothing.
Over-the-counter medications that may help include:
- Antacids: These neutralise stomach acid.
- H2 blockers: These reduce the amount of acid produced by the stomach.
- Proton pump inhibitors (PPIs): These block the production of stomach acid.
When should you see a doctor about heartburn?
- If heartburn occurs more than twice a week.
- Symptoms persist despite use of nonprescription medication.
- You have difficulty swallowing.
- You have persistent weight loss, nausea or vomiting.
If lifestyle changes and over-the-counter medications are not effective, your doctor may prescribe stronger medications or recommend surgery.
Surgery for a hiatus hernia used to be popular. It is now rarely done.
8. Complications
If left untreated, heartburn can lead to complications such as:
- Oesophagitis: This is inflammation of the oesophagus.
- Barrett’s oesophagus: This is a precancerous condition in which the cells lining the oesophagus change.
9. Prognosis
- The prognosis for heartburn is generally good. In most cases, it can be managed effectively with lifestyle changes and medication.
- However, if left untreated, it can lead to serious complications.
10. Prevention
- The best way to prevent heartburn is to make lifestyle changes, such as losing weight, eating smaller meals, and avoiding trigger foods and drinks.
Summary
We have described 10 facts about heartburn. We hope it has been helpful.
Top Tip
If the diagnosis is in doubt, an endoscopy should be considered.

