10 peptic ulcer facts
In this article we will describe 10 facts about peptic ulcers.
Key Points
-
Peptic ulcers are open sores that develop on the inside lining of the stomach and the duodenum.
-
The most common symptoms are epigastric pain and upper GI bleeding.
-
NSAIDs and Helicobacter pylori infection are major causes.
-
Diagnosis involves endoscopy and biopsy.
-
Treatment includes proton pump inhibitors, antibiotics, and lifestyle modifications.
1. Definition
- A peptic ulcer is a defect in the mucosal lining of the stomach or duodenum (the first part of the small intestine), resulting in an open sore.
Types
There are two main types:
-
Gastric Ulcer: Occurs in the stomach lining.
-
Duodenal Ulcer: Occurs in the duodenum.
2. Epidemiology
-
Approximately 4.4 million individuals are affected annually in the UK.
-
Duodenal ulcers are more common than gastric ulcers.
-
Men are more likely to develop peptic ulcers than women.
3. Risk Factors
-
Age: Risk increases after 40.
-
Family history.
-
Smoking.
-
Excessive alcohol consumption.
4. Causes
-
Helicobacter pylori (H. pylori) Infection: Bacterial infection leading to mucosal inflammation.
-
Nonsteroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs (NSAIDs): Long-term use of NSAIDs can erode the stomach lining.
5. Symptoms
-
Epigastric pain.
-
Upper GI bleeding (haematemesis or melena).
-
Nausea and vomiting.
-
Loss of appetite.
6. Diagnosis
-
Physical examination.
-
Medical history.
Investigation
-
Endoscopy: Visual examination of the stomach and duodenum.
-
Biopsy: Tissue sample analysis for H. pylori.
-
Barium Meal: X-ray examination using contrast material.
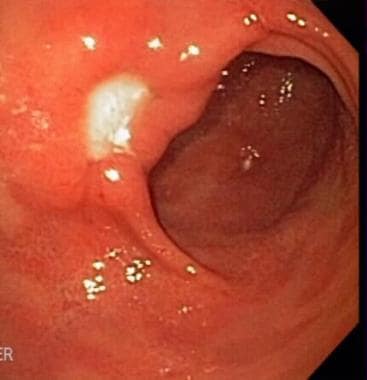 Peptic ulcer at endoscopy
Peptic ulcer at endoscopy
Differential Diagnosis
-
Gastro-oesophageal reflux disease (GORD).
-
Functional dyspepsia.
-
Inflammatory bowel disease.
- Gastric cancer.
- Gall stones.
7. Treatment
-
Proton Pump Inhibitors (PPIs): Reduce stomach acid.
-
Antibiotics: Eradicate H. pylori.
-
Lifestyle Modifications: Avoid NSAIDs, smoking, and excessive alcohol.
When to see a doctor with suspected peptic ulcer
-
Severe abdominal pain.
-
Vomiting blood or melaena (black tarry stools).
-
Difficulty swallowing.
8. Complications
-
Bleeding.
-
Perforation.
-
Obstruction.
-
Cancer.
9. Prognosis
-
Most peptic ulcers heal with treatment.
-
Recurrence is common if H. pylori persists.
10. Prevention
-
Avoid NSAIDs.
-
Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption.
Summary
We have described 10 facts about peptic ulcers. We hope it has been helpful.

