Appendicitis – patient information
We will now describe patient information about appendicitis.
Let’s start with some basics.
1. What is appendicitis? It is inflammation of the appendix
A small organ located in the lower right side of the abdomen. It is like a finger coming out of the side of the caecum; which is part of the right lower colon (bowel).

This means the appendix is usually in the right lower side of the tummy. But it can be in other places as human internal anatomy is not always the same.
Hence the presentation is not always with right lower abdominal pain and tenderness.
2. It is a common surgical emergency
And requires rapid treatment (surgery) to prevent complications, such as rupture (also called perforation) which means bursting of the appendix. Then bowel contents leak into the abdomen, causing peritonitis and severe pain. See below.
3. The exact cause of appendicitis is unknown
But it is believed to be due to a blockage or obstruction in the appendix.
4. Appendicitis can affect people of all ages
But it is most common in people between the ages of 10 and 30 years.
5. Symptoms
Initially include ‘colicky’ pain (this means one that comes and goes) in the centre of the abdomen – often with nausea, vomiting, fever, and loss of appetite.
But importantly, the symptoms of appendicitis can vary. And it can be hard to detect appendicitis in young children, older people, people on steroids, and women of childbearing age.
MyHSN has more on the symptoms of appendicitis.
6. The pain associated with appendicitis may then change
Even though it usually starts in the middle of the tummy, and is colicky (means comes and goes) in nature. It then usually moves to the lower right side of the abdomen, and becomes constant. This most often occurs 12 to 24 hours after the illness starts.
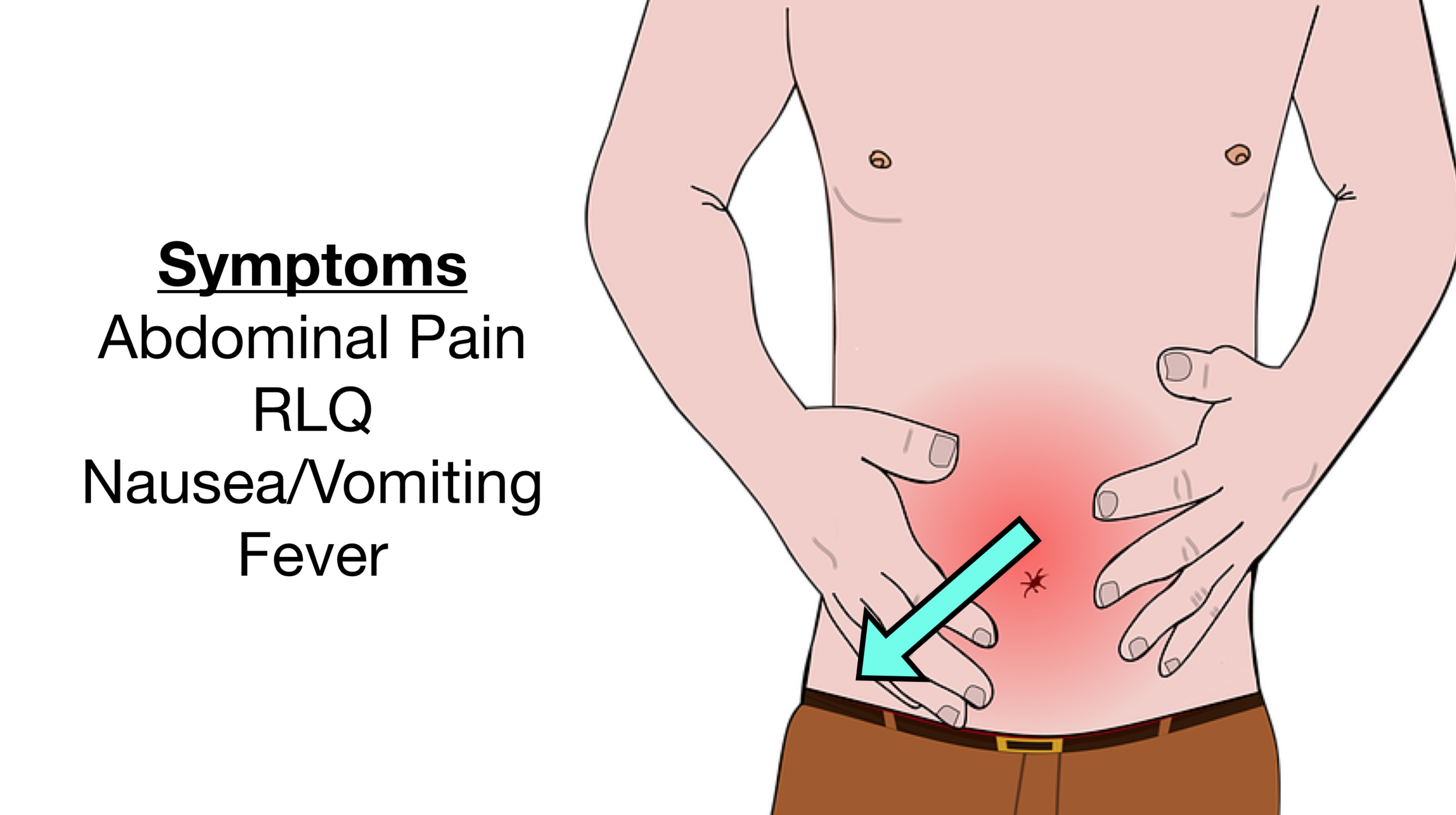
The pain and tenderness often finally settles on a spot directly above the appendix called McBurney point.
But. As they can point in many directions (or be on the left side in some people), this can give different clinical presentations – e.g. abdominal pain in different places.
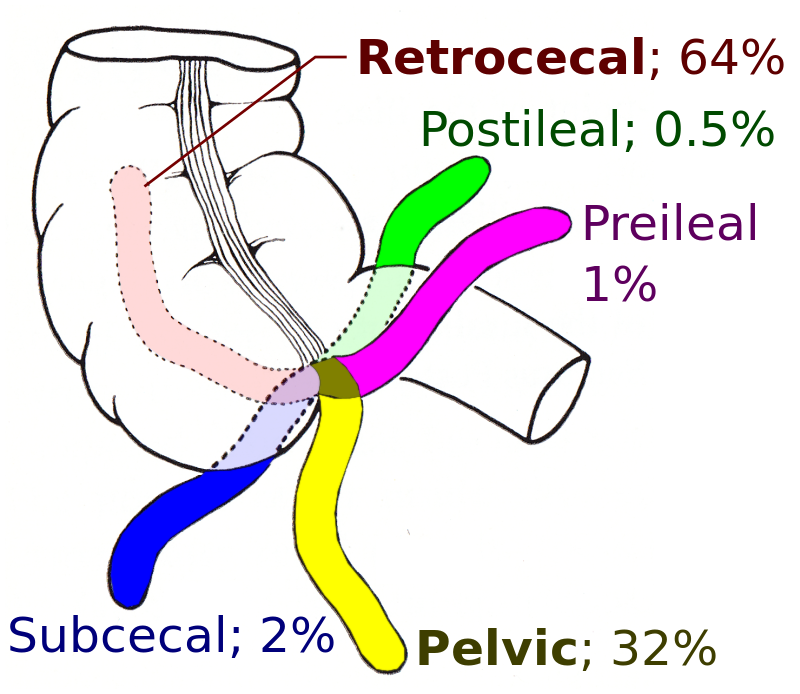 Different directions of the appendix
Different directions of the appendix
7. Diagnosis
Is usually made through a combination of a history (asking questions), physical examination, blood tests, and imaging studies such as an ultrasound or CT scan.
8. Treatment
Usually involves surgery to remove the inflamed appendix, which is called an appendectomy.
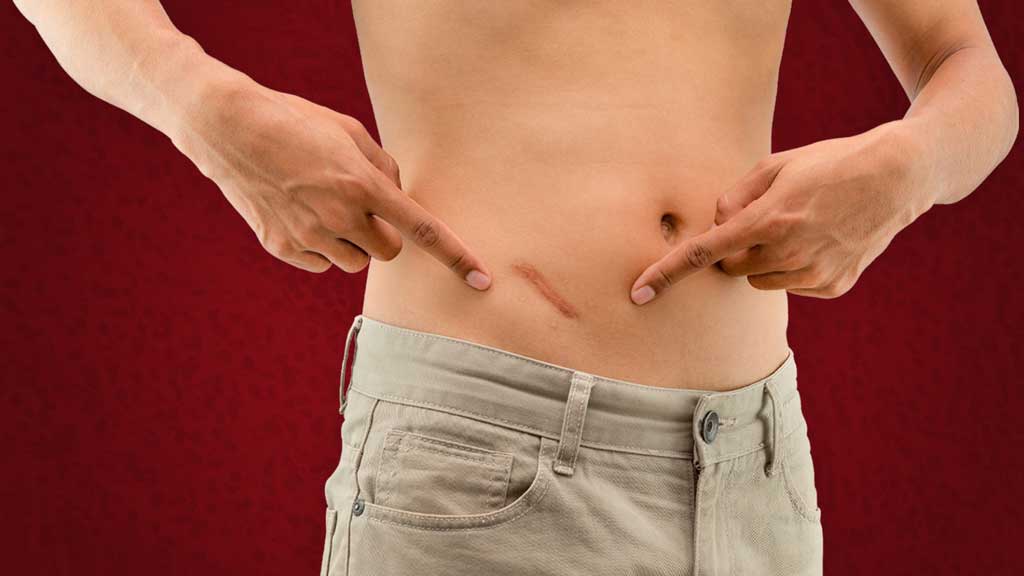 Surgery often leaves a scar like this one
Surgery often leaves a scar like this one
9. If left untreated
Appendicitis can lead to complications such as a ruptured appendix, which can cause a serious infection called peritonitis. This is life threatening.
10. Prognosis (outlook)
Most people with appendicitis recover fully and do not experience any long-term complications.
Summary
We have described patient information about appendicitis, based on 10 facts. We hope it has been helpful.

