Coeliac Disease (patient info factsheet)
In this article, we will describe 10 facts for patients about coeliac disease.
1. Definition
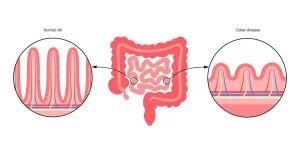
- Coeliac disease is a chronic autoimmune disorder that occurs when the body’s immune system reacts to gluten, a protein found in wheat, barley, and rye
- This reaction damages the lining of the small intestine, impairing nutrient absorption and leading to various health issues.
2. Cause
- The exact cause of coeliac disease is unknown, but it is believed to be triggered by a combination of genetic and environmental factors
- When individuals with a genetic predisposition consume gluten, their immune system mistakenly attacks the lining of the small intestine, causing damage and inflammation.
3. Risk Factors
Several factors increase the likelihood of developing coeliac disease:
-
Family history: Having a first-degree relative with coeliac disease
-
Genetic: Specific genetic markers, such as HLA-DQ2 and HLA-DQ8
-
Other autoimmune disorders: Conditions like type 1 diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, and autoimmune thyroid disease.
4. Who Gets Coeliac Disease?
- Coeliac disease affects people of all backgrounds
- It can develop at any stage of life, from infancy to adulthood
- It affects approximately 1 in 100 people worldwide.
5. Symptoms
The symptoms of coeliac disease vary widely and can include:
-
Diarrhoea or abdominal pain
-
Fatigue or weakness
-
Weight loss or gain
-
Nausea and vomiting
-
Bloating and gas
-
Pale or greasy stools.
Note. Some individuals may experience no noticeable symptoms, whilst others may have atypical symptoms, such as joint pain, skin rashes, or neurological issues.
6. Diagnosis
Diagnosing coeliac disease typically involves:
-
Blood tests: Measuring antibody levels in the blood to detect an immune response to gluten:
- IgA and IgG anti-tissue transglutaminase (tTG) antibodies
- IgA test
- Deamidated gliadin peptide (DGP) IgG test
- Intestinal biopsy: Examining a tissue sample from the small intestine for damage and inflammation. This is done in hospital, by a doctor called a gastroenterologist. A biopsy can help confirm a diagnosis of coeliac disease
-
Genetic testing: Identifying genetic markers associated with coeliac disease.
7. Treatment
- The primary treatment for coeliac disease is a strict gluten-free diet
- This involves avoiding foods that contain wheat, barley, and rye, and opting for gluten-free alternatives instead
- Nutritional supplements may also be recommended to manage deficiencies.
8. Complications
Untreated or unmanaged coeliac disease can lead to complications, such as:
-
Malnutrition: Impaired nutrient absorption can cause deficiencies and health problems
-
Osteoporosis: Poor calcium absorption can weaken bones
-
Increased risk of other autoimmune disorders
-
Intestinal damage: Prolonged inflammation can lead to permanent damage.
9. Lifestyle Changes
Adopting a gluten-free lifestyle requires significant changes:
-
Reading food labels carefully
-
Avoiding cross-contamination with gluten-containing foods
-
Exploring gluten-free recipes and ingredients
-
Informing friends, family, and healthcare providers about the condition.
10. Recurrence
- Coeliac disease is a chronic condition, and symptoms can recur if gluten is reintroduced into the diet
- Maintaining a strict gluten-free diet and monitoring symptoms can help manage the condition and prevent complications
- Regular follow-ups with your doctor are essential to ensure the effectiveness of treatment and address any concerns.
Summary
We have described 10 facts for patients about coeliac disease. We hope it has been helpful.

