What are the 10 most common blood thinning tablets?
In this article we will describe the 10 most common blood thinning tablets – starting with the oldest, aspirin.
Blood thinners limit coagulation, which prevent blood clots from forming. These include antiplatelet and anticoagulant drugs.
Blood thinners do not actually thin or change the viscosity of blood. But they are able to prevent clotting, which means they are used to help people, with a:
- Arterial blood clot – e.g. stroke, heart attack or clot in arm or leg
- Venous blood clot – e.g. deep vein thrombosis (DVT) or pulmonary embolus (PE)
- New heart valve
- Abnormal heart rhythm.
So. We will now go through the most commonly prescribed blood thinners.
Antiplatelet drugs
These work by preventing blood platelets from clumping.
1. Aspirin
2. Ticagrelor
3. Prasugrel
4. Clopidogrel
Anticoagulants
Low molecular weight heparins (LMWH; given as a subcutaneous injection, short or medium term treatment; do not require regular blood tests)
5. Enoxaparin – or dalteparin
Vitamin K antagonist (given as a tablet; long-term treatment; requires regular blood tests to check dose is correct)
6. Warfarin
Warfarin, the oldest anticoagulant drug, decreases blood clot formation by reducing the body’s level of vitamin K1, which regulates blood clotting.
Direct oral anticoagulants (DOACs) (tablets; long-term treatment; do not require regular blood tests)
7. Apixaban
8. Dabigatran
9. Edoxaban (betrixaban and rivaroxaban) – other DOACs
DOACs work by interfering with something called the coagulation cascade, and inhibiting clotting factors such as Factor Xa and Factor IIa.
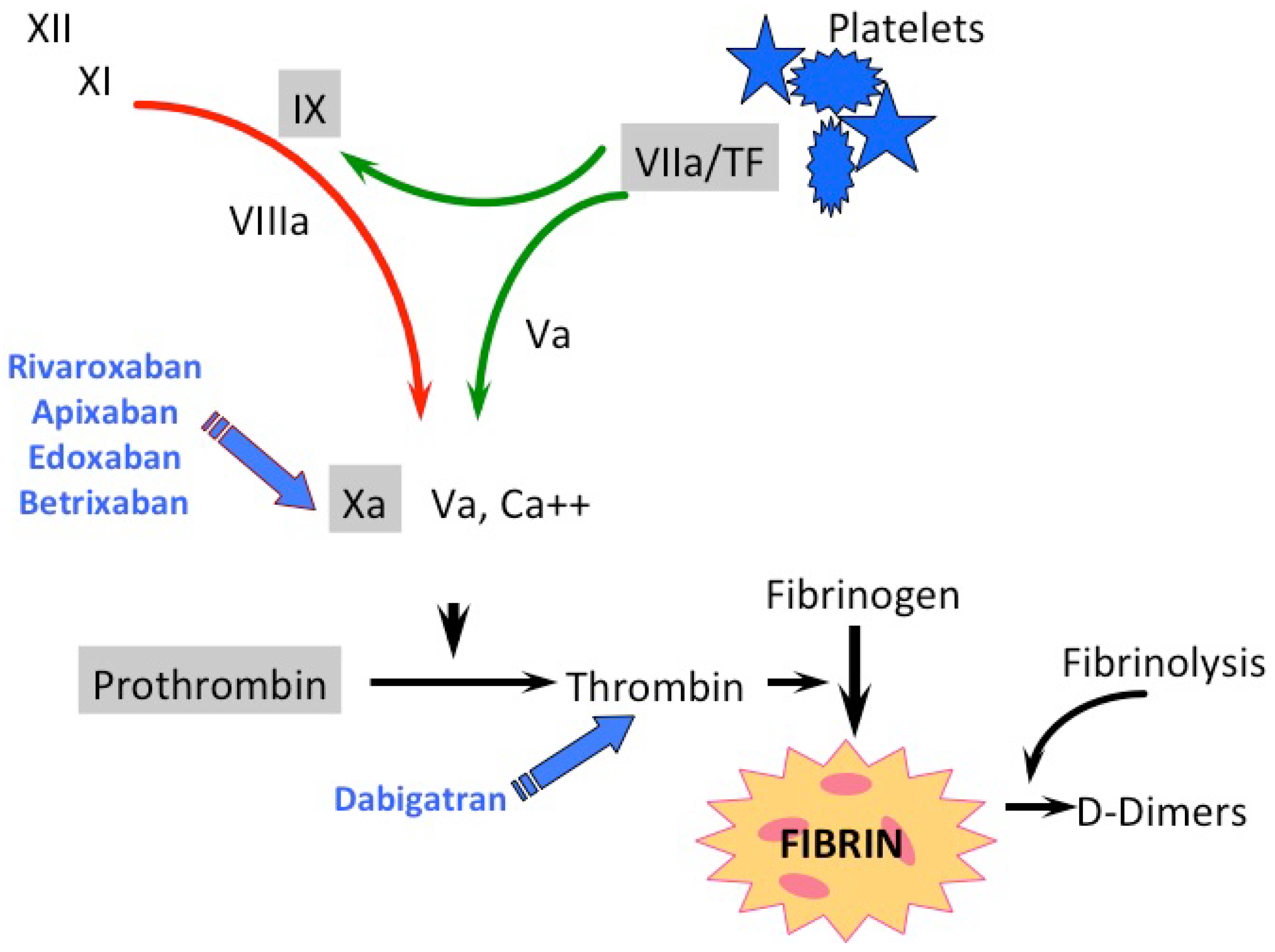 How DOACs work
How DOACs work
Thrombolytic drugs (injection; short term use)
10. Alteplase (tPA; tissue plasminogen activator)
Thrombolytic agents are used to break up dangerous blood clots – for example in a heart attack, stroke or pulmonary embolus.
Summary
We have described what are the 10 most common blood thinning tablets. We hope it has been helpful.

