What are the 5 different types of skin disease (with photos)?
There are 5 different types of skin disease. They can be categorised as either being caused by:
- Infection (bacterial, viral, fungal or parasites)
- Allergies (including drug)
- Autoimmune
- Cancer
- Genetic.
Here are examples of the 4 different types of skin disease:
1. Infections
Bacterial infections
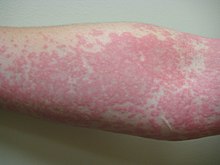
Cellulitis – a common infection caused by bacteria entering a break in the skin. It is caused by Group A ß-hemolytic streptococcus (‘Strep A’), Streptococcus pneumoniae (‘Strep’), Staphylococcus aureus (‘Staph’), and Methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus (MRSA).
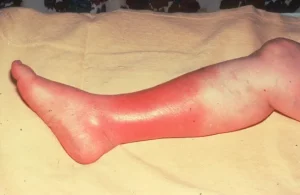
It causes swelling, pain and redness. If it is not treated, cellulitis can be very serious, especially if it infects the eye (orbital cellulitis). It requires treatment with antibiotics, sometimes IV and in hospital.
Note. Strep A also causes ‘Strep throat’, acute rheumatic fever and post-streptococcal glomerulonephritis.
Impetigo – is skin infection caused by bacteria, usually Staphylococcus or Streptococcus. It is highly infectious and itchy, it tends to manifest as red sores. It is more commonly seen in children and babies than adults. It can appear anywhere on the body, but is more common around the nose and mouth. Topical treatments, as well as oral antibiotics are used to treat impetigo.
Boils and carbuncles – infections of hair follicles or oil glands that develop as a sore lump over a few days, eventually filling with pus. A carbuncle is a painful concentration of boils linked to each other beneath the skin. If these boils/carbuncles become very large and painful, your doctor may need to drain it. Antibiotics – sometimes in hospital – may be prescribed if the patient suffers from recurrent infections, or if they are particularly severe.
Viral infections
Warts – generally harmless lesions caused by Human Papillomavirus (HPV) that eventually clear up without treatment, but take a long time to do so. There are also a number of treatments available, including freezing them, acid treatments, laser treatments or gels.
Verrucas – A type of wart that commonly appears on the foot (plantar wart). They sometimes have a black dot in the middle of them, and can cause a lot of pain when walking. Most verrucas go away on their own, but if they are painful you may want to remove them. There are a number of different gels available to treat verrucas. They can also be frozen.


Cold sores – caused by the herpes simplex virus (HSV), these sores usually appear on the mouth. They are contagious, so you should avoid kissing people or having sex until the sore has completely healed. This usually takes about 10 days, but there are also antiviral medications and ointments available to treat them.
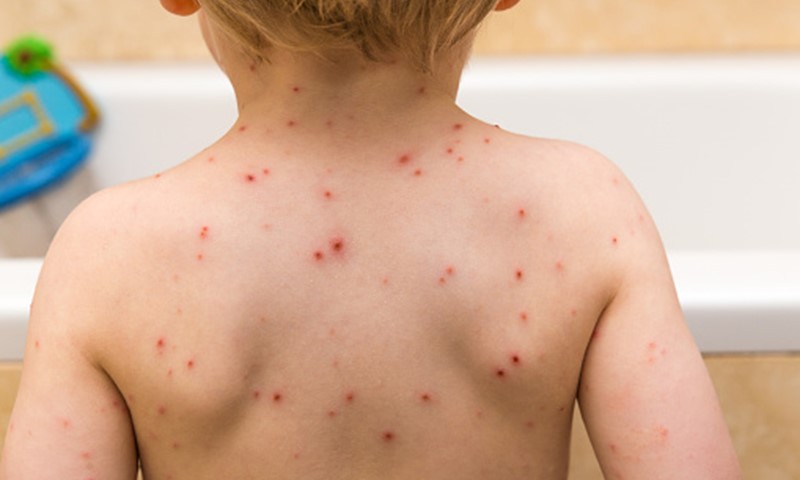
Chickenpox – a common infectious disease known for the red, itchy spots it causes. It is caused by Varicella-Zoster Virus (VZV). It is most common among children, but can affect people of any age. It can also cause fever or aches and pains. They are very contagious and your child should stay home from school if they have chicken pox. It usually takes 2 weeks for chicken pox to heal. A number of topical treatments can help ease symptoms.
Shingles – a reactivation of the dormant Varicella-Zoster Virus (VZV), shingles causes clusters of painful blisters. It only occurs in people who have already had chickenpox. It can take up to a month for a shingles rash to heal. Paracetamol or other painkillers can be taken to help ease the painful symptoms. It can be very painful, sometimes for weeks and months after the rash has gone.

Fungal infections
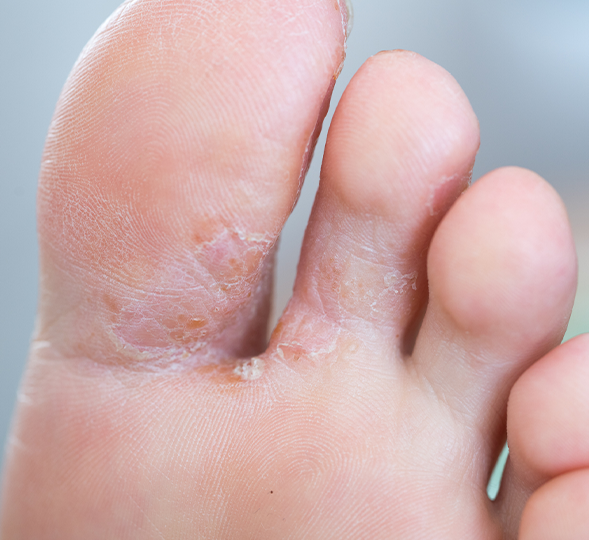
Ringworm (including athlete’s foot, tinea pedis) – not a worm, as it’s name suggests. There are different types in different areas of the body. It usually appears as a red, scaly patch that itches. It may appear in a ring or bump. It can be treated by antifungal creams or powders.
Yeast infection (candidiasis) – caused by the candida fungus, which naturally appears in small amounts on the body. Infections occur when the yeast builds up and grows out of control. Infections in the mouth and throat are called ‘thrush’. Candida can be treated with antifungal creams, powders or medication.

Parasitic infections
Scabies – an infestation of mites that burrow into the skin and lay eggs, causing a rash and intense itching. Scabies are usually spread through sexual or prolonged skin-to-skin contact. In rare situations, it can be spread by sharing bedding, towels or clothes. There are a number of creams and lotions used to treat scabies.

Bedbugs – tiny parasitic insects that suck human blood, preferring warm environments, such as beds. You may notice spots of blood on your sheets. In order to get rid of bed bugs, a pest control service should be contacted. A pharmacist can also give you topical treatments for the bites.
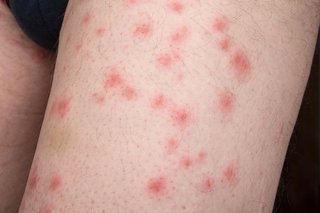
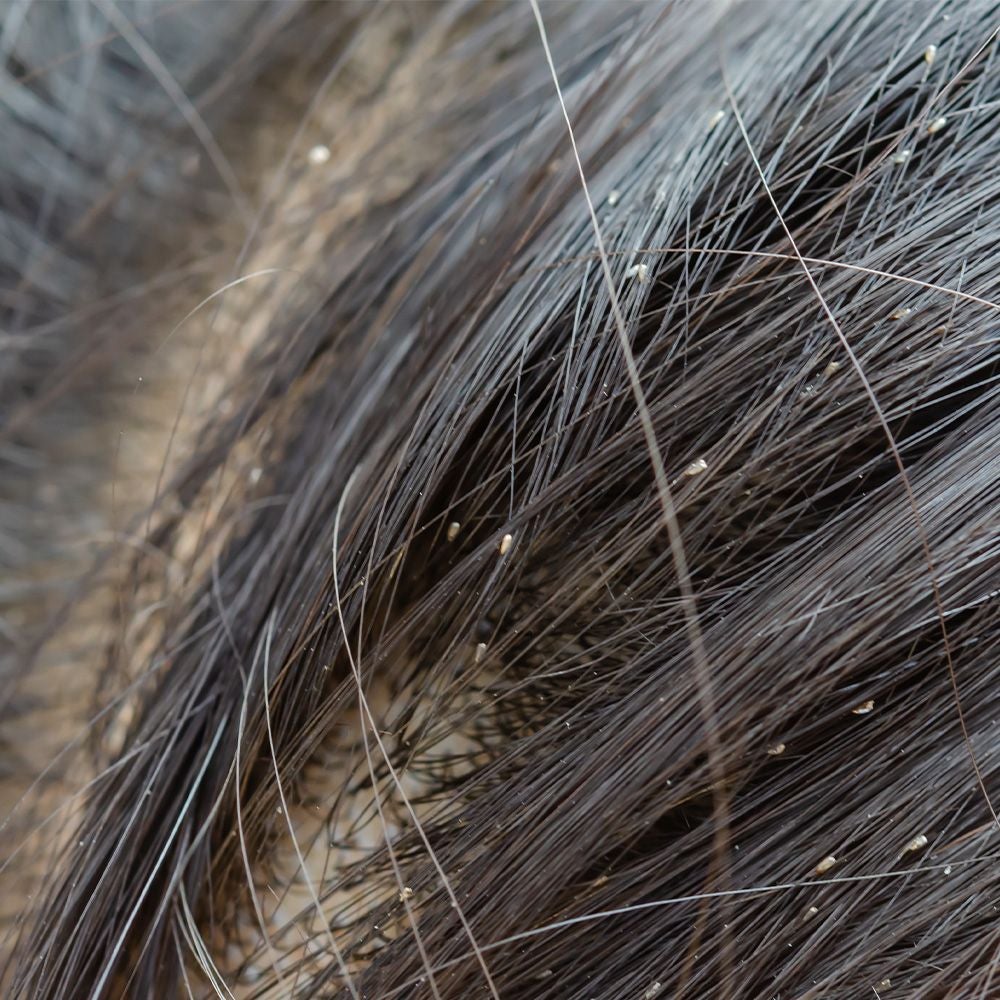
Headlice – tiny, wingless insects that live in the hair, drinking blood from the scalp. They are commonly found on the hair of children, with schools frequently experiencing outbreaks. Their eggs (nits) are often found attached to the hairs of the patient. Treatments usually include a lotion or shampoo that kills the eggs and lice.

2. Allergies
Hives (urticaria) – a raised, itchy rash. Can be causes by allergies, and also by insect bites, nettle stings etc. It can also be triggered by stress, hot weather, caffeine or alcohol. Hives usually go away on their own within a few days, but steroids may be prescribed if it is a severe case. Antihistamines can help ease the itching.
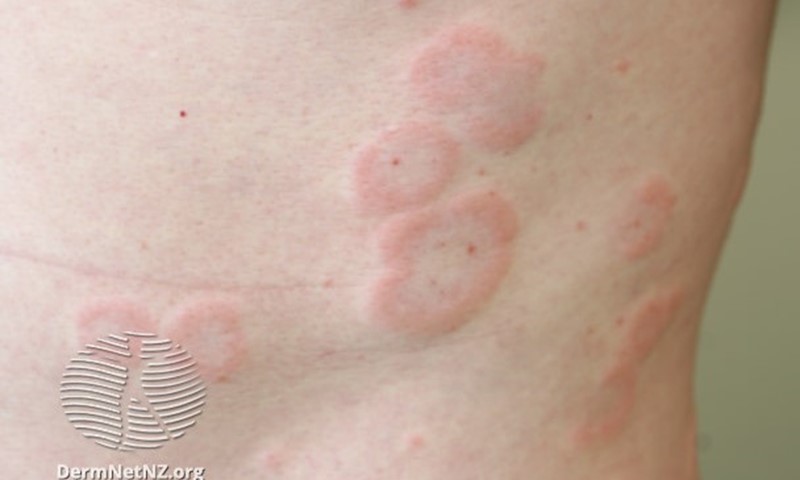
3. Autoimmune
Eczema – causes the skin to become red, dry, cracked and sore. Avoiding triggers can help lessen atopic eczema episodes. Topical corticosteroids are also often used to lessen symptoms. Keeping the skin moisturised can also help.

Psoriasis – characterised by flaky, red silvery patches of skin. It can run in families. There are a number of different topical treatments available to help ease the symptoms.
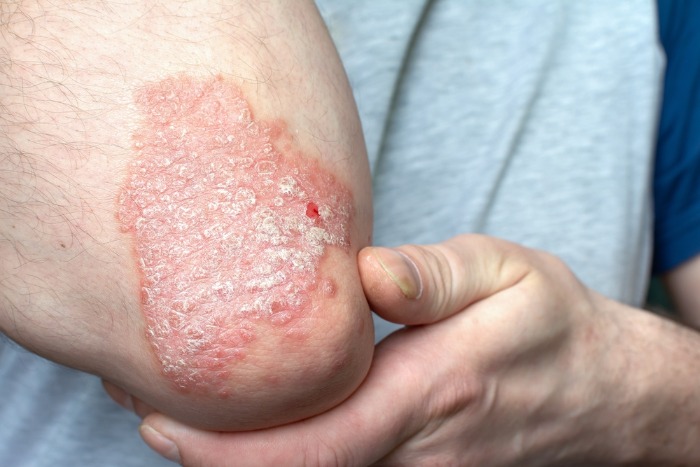
4. Cancer
Basal cell carcinoma
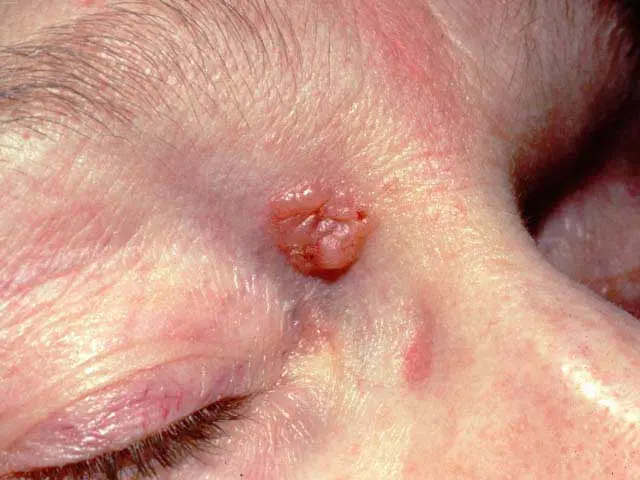
- It can cause dome-like, pink or red, shiny, and pearly areas that may have a sunk-in centre, like a crater. For people with dark skin, it might appear darker and less pearly
- This condition is often characterised by raised, firm, and pale areas that may resemble a scar
- They often occur on the face, especially near the eyes and nose
- Blood vessels on the growth may be visible
- It might cause easy bleeding or an oozing wound that doesn’t seem to heal, or it heals and then reappears.
Squamous cell carcinoma
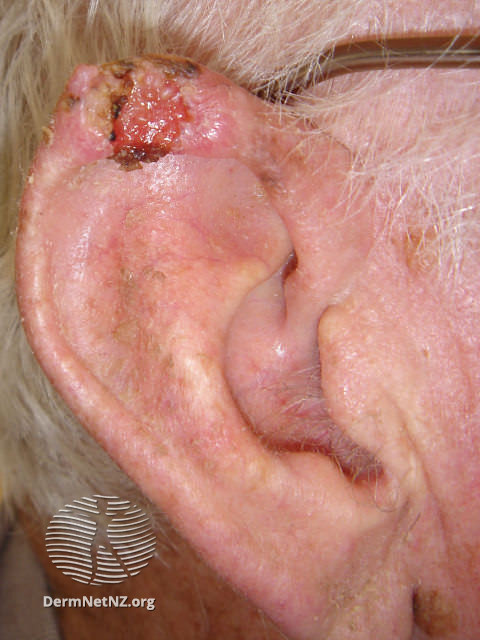
- This condition often occurs in areas exposed to ultraviolet (UV) radiation, such as the face, ears, and back of the hands
- They are characterised by a scaly, reddish patch of skin, which progresses to a raised bump that continues to grow. The bump may be lighter on darker skin
- It can also cause a growth that bleeds easily, does not heal, or heals and then reappears.
Melanoma
- This is the most serious form of skin cancer, which is more common in people with light skin
- It can appear anywhere on the body as a mole that has irregularly shaped edges, asymmetrical shapes, and multiple colours.
5. Genetic
These are some genetic skin disorders, fortunately all rare.
Basal cell nevus syndrome or Gorlin syndrome – a rare genetic condition that involves the skin, nervous system, eyes, bone structure and endocrine glands with risks of numerous basal cell carcinomas and jaw cysts.

Muir-Torre syndrome – a hereditary condition characterised by sebaceous tumors of the skin and the potential for developing internal malignancies, most often colon cancer.
Cowden syndrome – a rare, inherited condition that causes multiple benign tumour-like growths and increased risk for breast, thyroid and uterine cancers. Common characteristics include an enlarged head size and trichilemmomas on the skin, face, hands, mouth and mucous membranes.
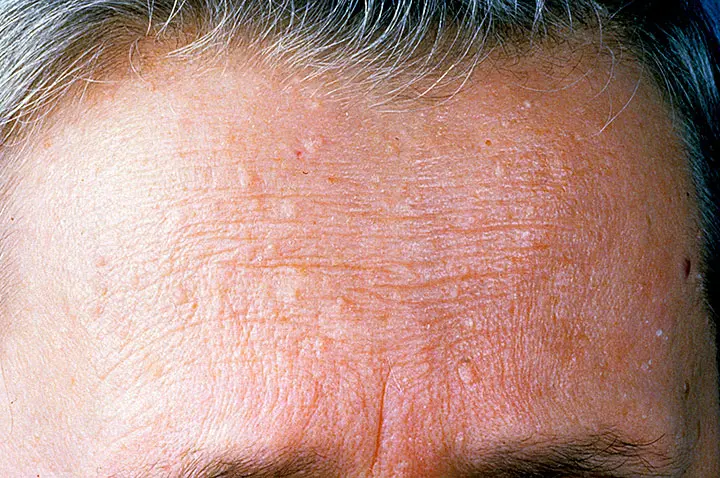
Tuberous sclerosis – a genetic disorder that affects the skin, brain and nervous system, kidneys and heart. Collagenomas, ash leaf macules and angiofibromas are common skin findings.
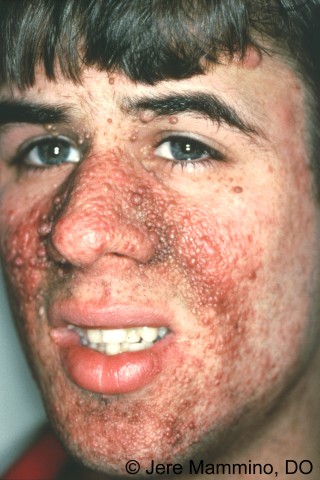
Neurofibromatosis – a genetic disorder of the nervous system and skin. The disease is characterised by findings that include café au lait patches, axillary freckling and numerous neurofibromas.


Gardner syndrome – a rare, genetic disorder characterised by multiple polyps in the colon, extra teeth, bony tumors of the skull and fatty cysts and/or fibrous tumours in the skin.
Summary
We have described the 5 different types of skin disease, and provided photos. We hope it has been helpful.