What do the tonsils do (5 functions)?
In this article we will describe what do the tonsils do, and explain their 5 functions.
1. Four types
Tonsils are an important part of the immune system. They are glands at the back of the throat and tongue.
People have four kinds of tonsils: palatine tonsils (visible at the back of the throat), lingual tonsils (at the base of the tongue), tubal tonsils, and adenoid tonsils
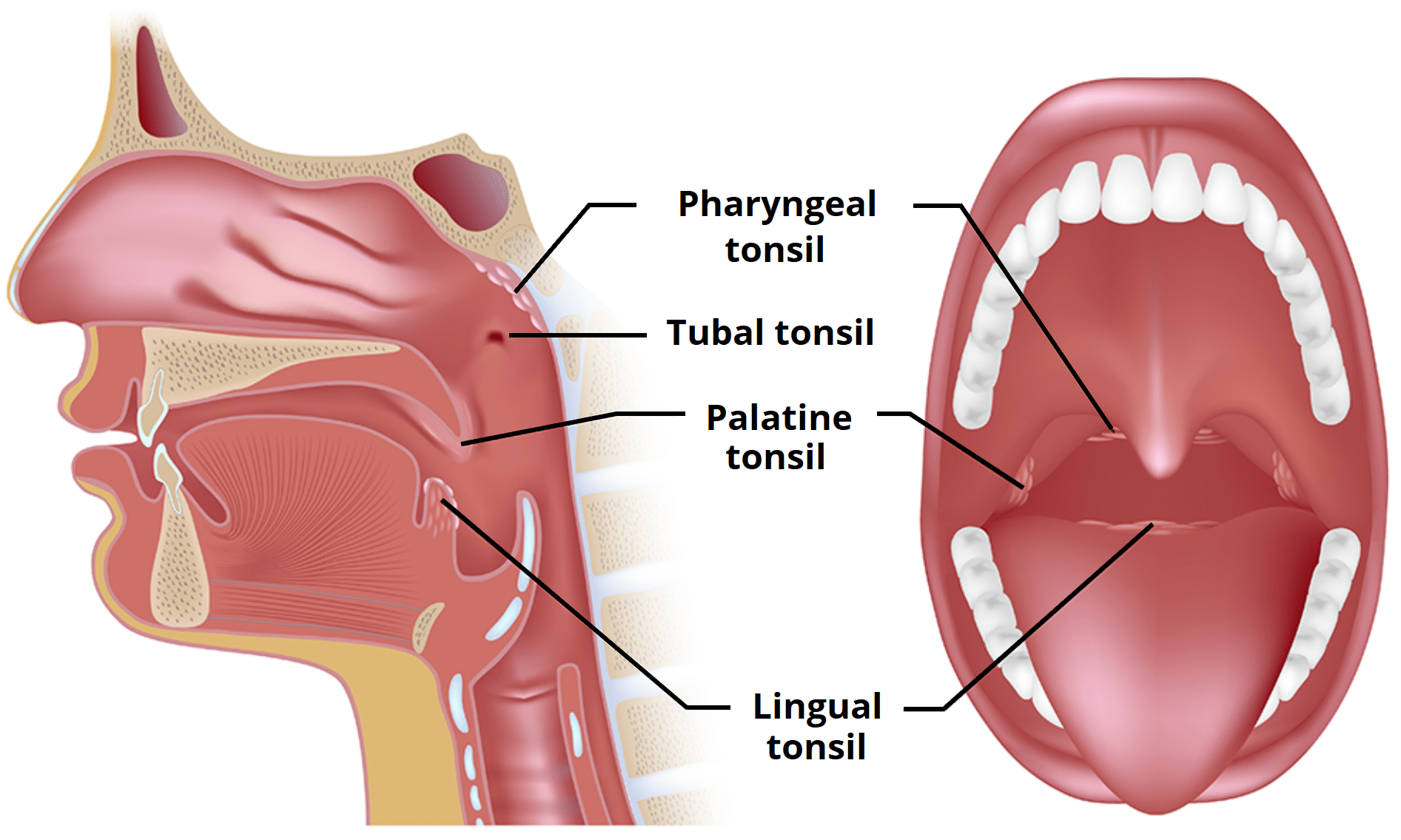
Collectively, the tonsils form a ring of lymphoid tissue known as Waldeyer’s ring.
Note 1. The 2 palatine tonsils are the ones you can see
One may be larger than the other
Note 2. The pharyngeal tonsil is also called the adenoid. There is one of them.
2. What do the tonsils do?
The tonsils have 5 important functions, all as part of the body’s immune system:
- Pathogen trapping. Tonsils act as a first line of defense by trapping pathogens (bacteria and viruses) that enter the body through the mouth or nose
- Immune response activation. They contain immune cells, such as white blood cells, which help to detect and fight off infections
- Antibody production. Tonsils produce antibodies that help neutralize pathogens, preventing infections from spreading further into the body
- Immune system development. Especially in children, tonsils play a role in the development of the immune system by exposing it to various pathogens and helping it learn to respond
- Lymphoid tissue. Tonsils are part of the lymphatic system, which helps to filter out harmful substances and support immune function.
3. Colour and health
Healthy tonsils are pink, but they can become red and swollen when infected
4. Size variation
Tonsil size varies significantly among individuals, with an average size slightly larger than a marshmallow
5. Tonsils shrink over time
Tonsils are larger in children and often shrink during adolescence. By adulthood, they become much smaller and may not be as active in immune responses
6. Tonsillitis
Tonsils can become infected, leading to a condition known as tonsillitis, which can be caused by both bacteria and viruses. Tonsillitis which is one of the common causes of a sore throat, is common in children. They may get recurrent attacks. It usually gets better eventually
7. Tonsillectomy
Tonsil removal, or tonsillectomy, used to be a common operation (especially in children), for those with chronic tonsillitis. Now the immune function of the tonsils is known, it is now less common.
Enlarged tonsils can block the airway during sleep, contributing to snoring. Tonsillectomy can also be done for obstructive sleep apnoea (OSA)
8. Ancient surgery
Tonsillectomies have been performed for thousands of years, with references found in ancient Ayurvedic texts
9. Adenoid tonsil issues
Enlarged adenoid tonsils can obstruct breathing and cause facial deformities in children if not treated
10. Tonsil stones
Tonsils can develop small calcified deposits known as tonsilloliths or tonsil stones, which form in the crevices of the tonsils and can cause bad breath.
Summary
In this article we have described what do the tonsils do, and explained their 5 functions. We hope it has been helpful.

