In this article, we will describe what does the heart do (7 facts). We hope it is useful.
It is located in the chest cavity, to the left of the sternum.
The heart is susceptible to various diseases and conditions; including ischaemic disease (IHD; angina and heart attacks), congenital and valvular heart disease, chronic heart failure (CHF), and arrhythmias (especially atrial fibrillation, AF).
In an adult and weighs around 250 to 300 grams; compare that to the heart of a blue whale, which is 200 kg.
These are the right atrium, the left atrium, the right ventricle, and the left ventricle.
The atria receive blood while the ventricles pump blood out.
There are four valves in the heart that keep the blood flowing in the correct way – they are vulnerable to an infection called endocarditis.
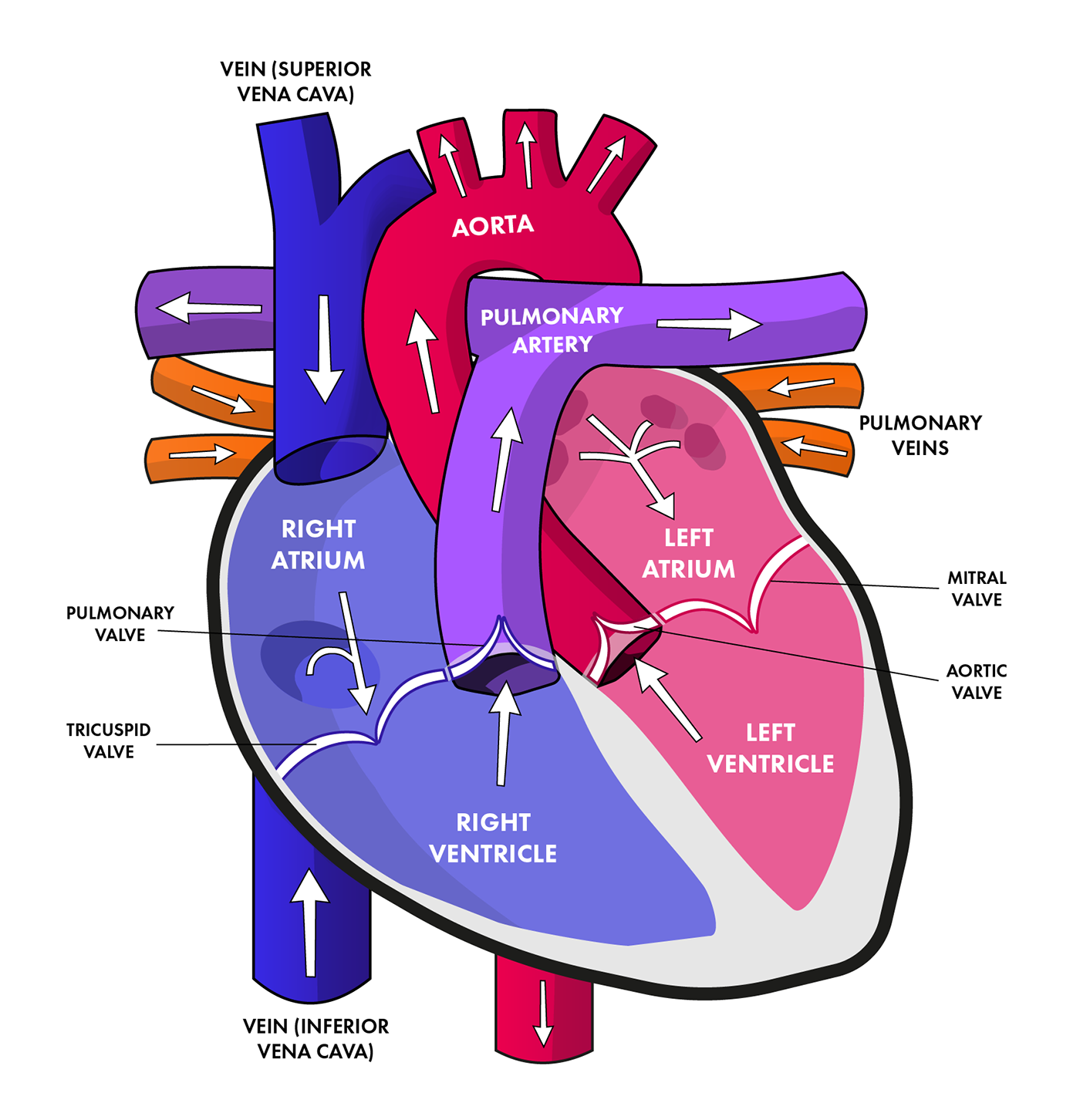 Heart anatomy
Heart anatomy
Hence the heart beats around 100,000 times a day; continuously pumping around 5 litres (8 pints) of blood through the body.
A heart rate of 60 beats/min or under is called a bradycardia; over 100 beats/min is a tachycardia.
A heart rate of 40 BPM at rest may be normal in an athlete. 150 BPM is normal if you are exercising hard.
This contains a small amount of fluid to help cushion and protect the heart.
This can be affected by an acute or chronic inflammation called pericarditis. There are many causes including viral and tuberculosis.
These branch off the aorta and wrap around the heart.
The sinoatrial node (SAN; sino for ‘sinus’), also known as the ‘pacemaker’, is a group of specialist cells that sends electrical impulses to the heart muscle. These impulses pass to the atrioventricular node (AVN), and the whole system causes contraction of the heart.
We have described what does the heart do? (7 facts). We hope you understand it better now.