What is CRP (C-reactive protein)?
C-reactive protein (CRP) is a protein produced by the liver that increases in response to inflammation in the body, serving as a marker for inflammation, infection and other disease processes.
CRP is an acute-phase reactant protein, meaning its levels rise rapidly in response to inflammation.
How it works
When the body experiences inflammation (due to infection, injury, or certain diseases), the liver produces and releases CRP into the bloodstream.
How quickly does CRP go up and go down again?
This is summarised in this diagram. It comes down if the cause is getting better.
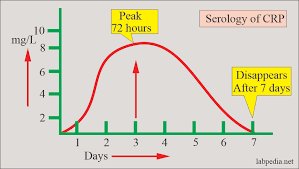
Note. CRP starts rising at 4-6 hours, i.e. soon after the onset of the disease process.
Why it’s important
Elevated CRP levels can indicate the presence of inflammation, which can be a sign of various conditions, including infection, autoimmune disease, tissue injury, malignancy – and even increased risk of cardiovascular disease.