When should you see a doctor about a bite or sting?
Most bites (by animals or humans) or stings are not serious and you don’t need to see a doctor. They will get better within a few hours or days.
But occasionally they can become infected, cause a severe allergic reaction (anaphylaxis) or spread serious illnesses such as Lyme disease and malaria.
Bugs that bite or sting include wasps, hornets, bees, horseflies, ticks, mosquitoes, fleas, bedbugs, spiders and midges.
Symptoms of an insect bite or sting
Insect bites and stings will usually cause a red, swollen lump to develop on the skin. This may be painful and in some cases can be very itchy.
Some people have a mild allergic reaction and a larger area of skin around the bite or sting becomes swollen, red and painful. This should pass within a week.
Occasionally, a severe allergic reaction can occur, causing symptoms such as breathing difficulties, dizziness and a swollen face or mouth. This requires immediate medical treatment.
What to do if you have been bitten or stung
- Remove the sting or tick – if it is still in the skin
- Wash the affected area – with water and soap
- Apply a cold compress (such as a flannel or cloth cooled with cold water) or an ice pack); if it is large or painful after a few hours, to any swelling for at least 10 minutes. Raise the affected area if possible, as this can help reduce swelling
- Avoid scratching the area – to reduce the risk of infection
- Avoid traditional home remedies – such as vinegar and bicarbonate of soda, as they’re unlikely to help
The pain, swelling and itchiness can sometimes last a few days. Ask your pharmacist about medicines that can help, such as painkillers, creams for itching and antihistamines.
But you should see a doctor, if you have any of the following symptoms:
- Infection – if there is pus, increasing pain, swelling, or redness around the bite
- Widespread infection – you have a high temperature, swollen glands, or other flu-like symptoms
- Allergic reaction – you have had a serious allergic reaction to an insect bite or sting before
- Severe pain – you have severe pain that doesn’t improve after taking pain medicine
- Redness – there is new redness around the bite appears more than 24 hours after the bite, or the redness gets larger after 48 hours
- Bite location – you were bitten in your mouth, throat, or near your eyes
- Tick bite – you can’t completely remove the tick, or the tick has been under your skin for more than 24 hours.
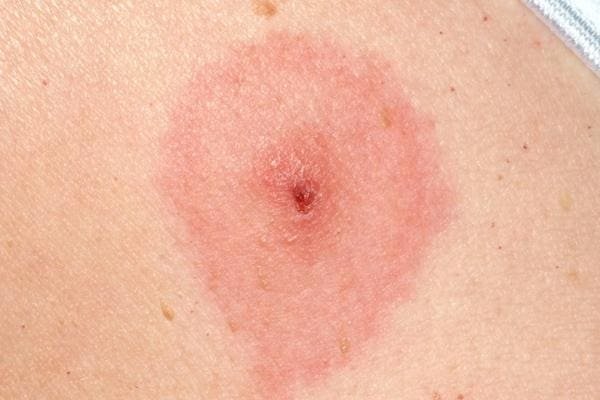
Tick bite. If you see a tick, remove it. You may need tweezers.
Children, the elderly, and people with compromised immune systems are more likely to have severe reactions to bites.

